Traditional medicine practices worldwide
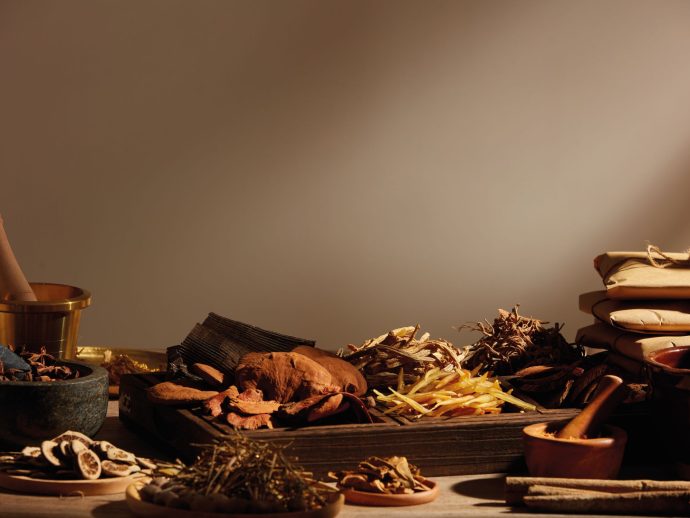
Traditional Chinese medicine
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) revolves around qi, a concept in Chinese culture describing the energy that flows through everything. An imbalance of qi can cause disease. The ancient Chinese believed that good health comes down to achieving an equilibrium between your internal organs and natural surroundings. Acupuncture, tai chi, and cupping therapy are all TCM modalities.
Traditional Indian medicine
In India, traditional medicine is divided into three categories: Ayurveda, Siddha, and Unani. Ayurveda, the most used, is a holistic, personalized system aimed at promoting longevity. As in TCM, Indian medicine is centred on balancing bodily organs and external elements.
Traditional Indigenous medicine
For centuries, Indigenous populations in North America have practised their own traditional forms of wellness through ceremonies; plant, animal, or mineral-based medicines; energetic therapies; and physical or hands-on techniques, all of which rely upon an emphasis on Mother Earth.
Traditional African medicine
Traditional African medicine is deeply rooted in the spiritual, with many practitioners using divination to connect with the gods and ancestral spirits for diagnosis before treatment with herbal medicines.
How is traditional medicine different?
Traditional medicine is often treated as pre-scientific, but a lot of conventional medicines come from plants. For example, aspirin was derived from the bark of a willow tree and morphine is extracted from the opium poppy, while vincristine—long-used in chemotherapy treatments—was isolated in 1961 from a Madagascar periwinkle flower.
Benefits of traditional medicine
One of the key benefits of traditional and alternative medicine is its holistic approach to health. Alternative medicine practitioners often spend over an hour with a patient each session, addressing a myriad of different concerns, says Poulton.
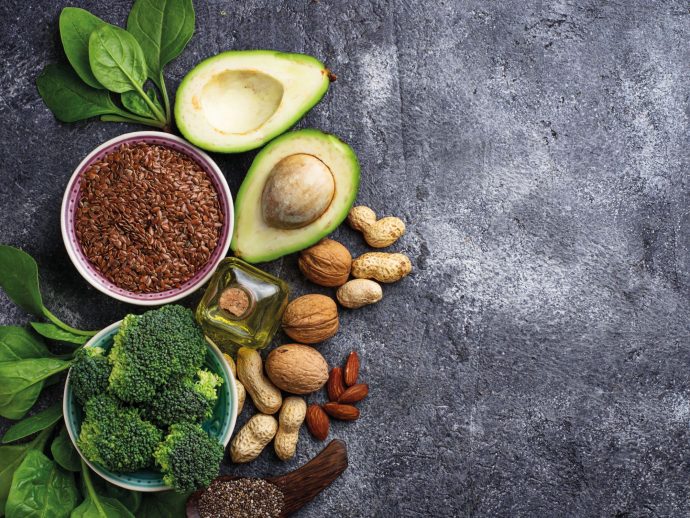
Complementary and alternative medicines
| Herb | Uses [CHARTHEADS] |
| garlic | may help reduce inflammation, cholesterol, blood pressure, and blood sugar levels and to help support immunity |
| ginger | may help treat nausea, heartburn, and bloating; may help reduce inflammation |
| elderflower | is used to help treat colds, flu, and constipation; may help lower blood pressure |
| ginseng | may boost energy and sex drive |
| shea butter | is anti-inflammatory; protects skin cells; is used to treat skin and eczema |
| ashwagandha | may reduce inflammation, pain, and anxiety |
| cumin | may help reduce cholesterol; may help maintain healthy blood sugar levels |
| turmeric | may help treat arthritis pain, anxiety, and inflammation |
| cardamom | may help treat nausea; may help to reduce blood pressure, blood sugar, inflammation |
| echinacea | may help treat colds, flus, infections, and wounds |